DATA 505: Statistics Using R
Week 5: Data manipulation & visualization
Prof. Yi Lu
2025-12-09
Prep work
The following packages are required for today’s lecture. Please install first if needed.
To start, we’ll use a very simple dataset in Base R.
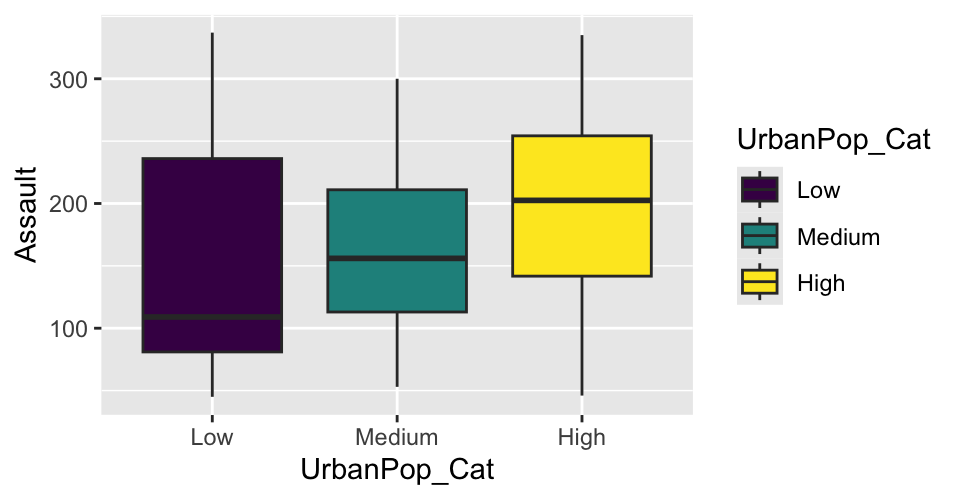
Create a separate variable for state names; create a categorical (ordinal) variable based on Urban Population. More on this syntax later.
Base R plots
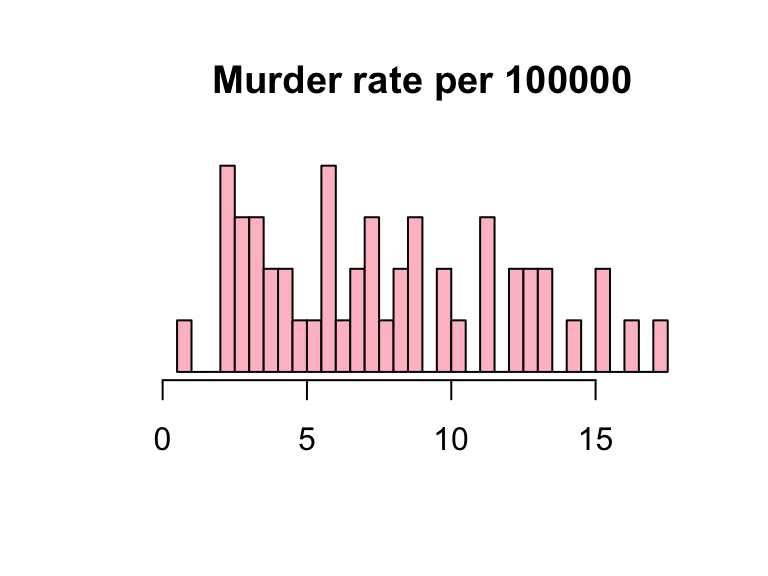
Histogram
- Histogram is a uni-variate graph. To describe a distribution, keep in mind properties of location, spread, and shape.
- Visualization elements can be modified by adding arguments within the function
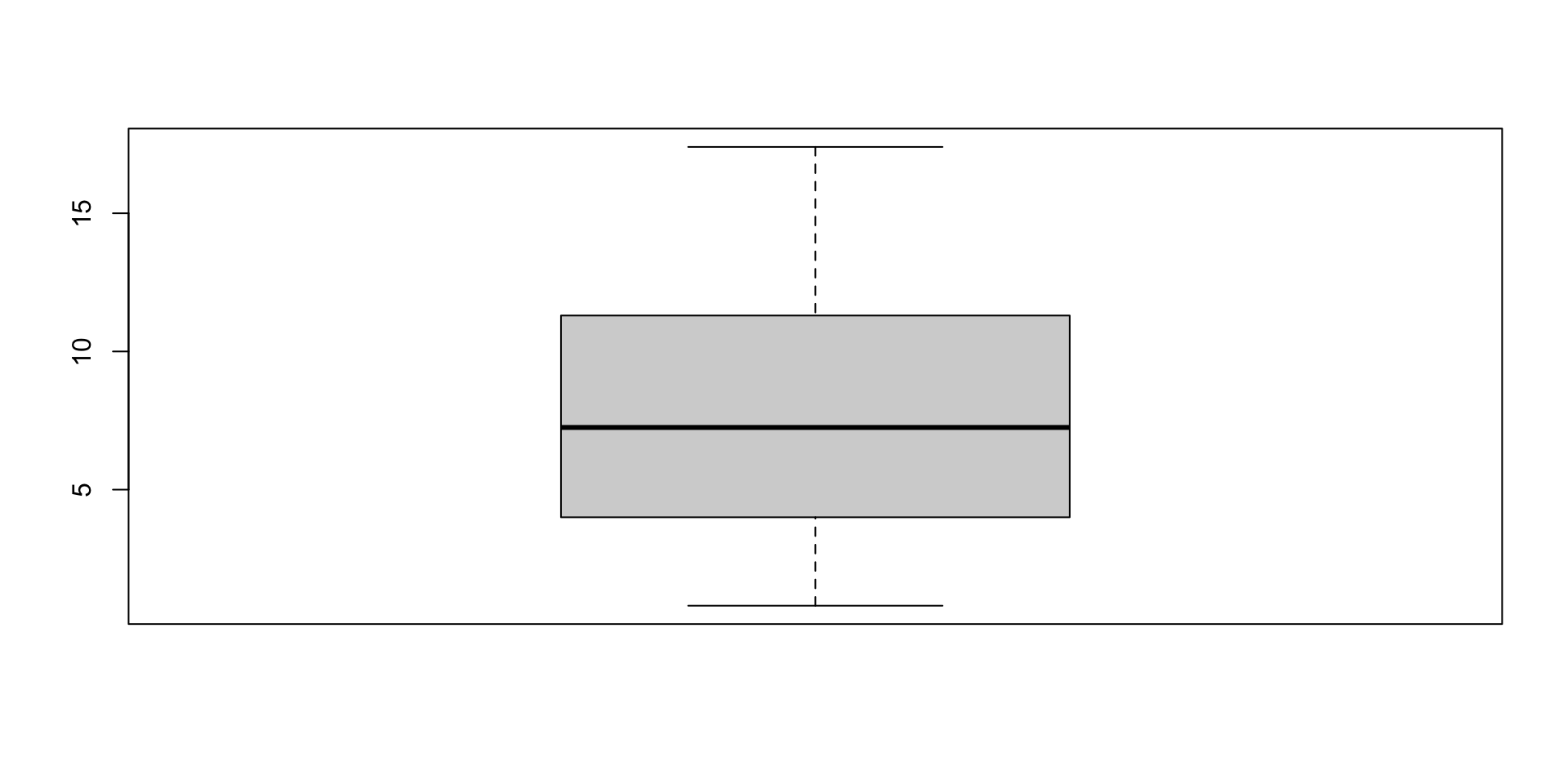
Boxplot
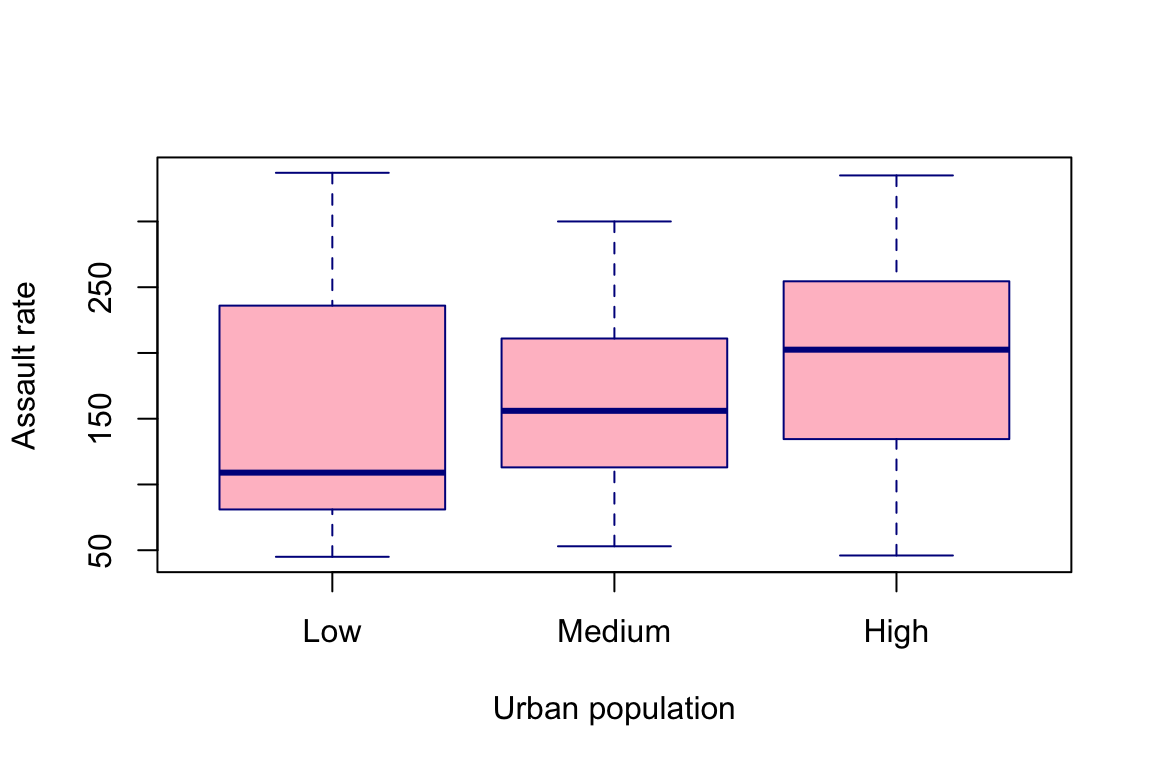
- Boxplot is based on the 5-number summary: min, Q1, Q2 (median), Q3, max
Stem and leaf plot
Side-by-side boxplots
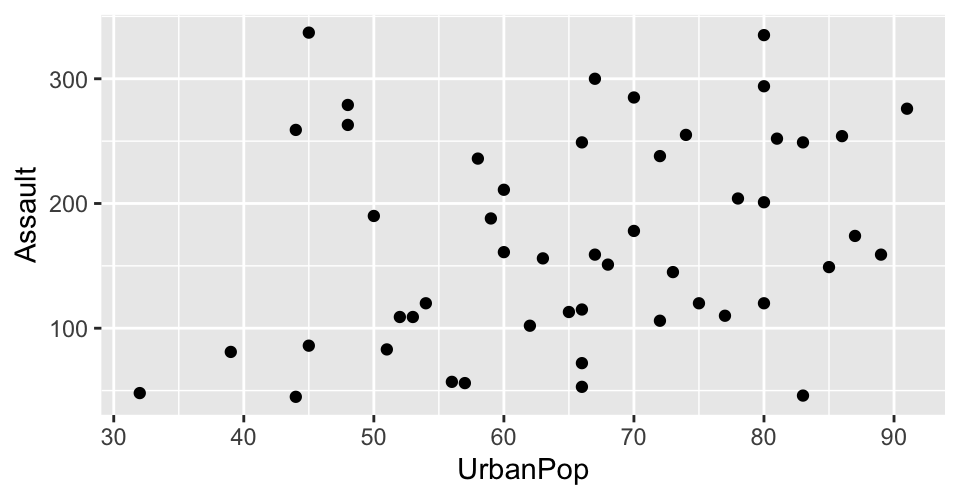
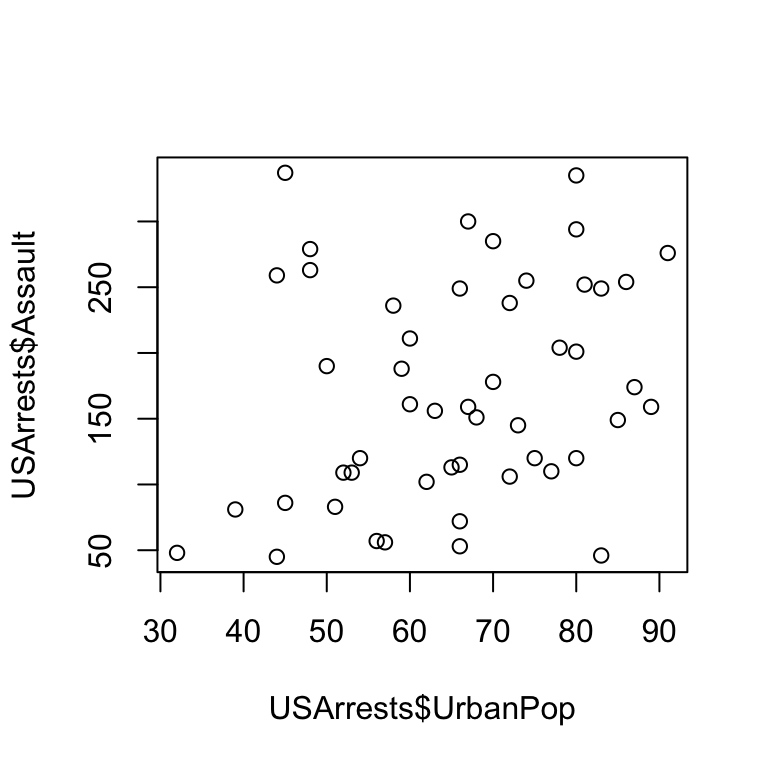
Scatterplot
- Scatterplots are bi-variate; useful to detect relationship between two numeric (scale) variables
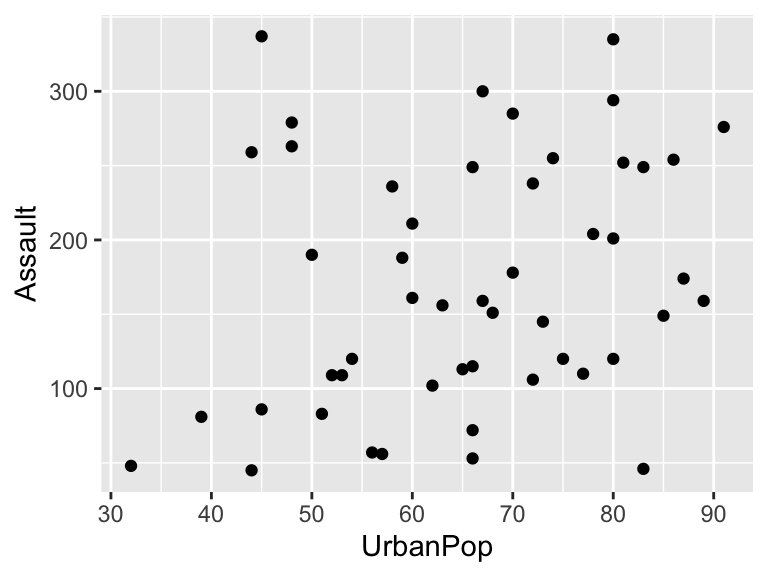
ggplot2
Example 1
- ggplot2 is an alternative, more unified framework (Grammar of Graphics) for creating plots and graphics in R
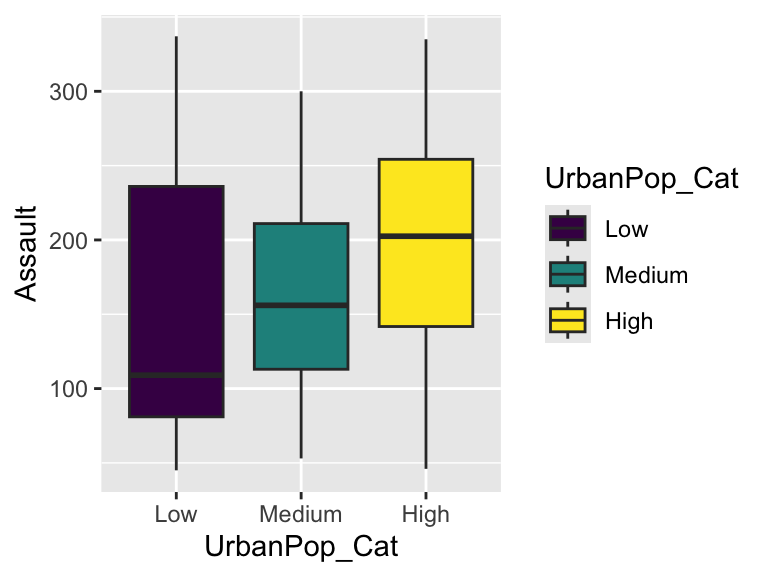
Example 2
Basic ingredients of a ggplot
- Data
- Data frame containing all the raw observations
- Aesthetic mapping
- An aesthetic is a visual property of the plot, such as x-axis, y-axis, color, fill, size, etc.
- Use aes to specify which variable is mapped to which aesthetic
- Example: height -> x-axis; weight -> y-axis; gender -> fill; name -> text
- Geoms
- What types of layers should be added to the plots
Example 1 explained
Example 2 explained
geom_histogram
- Recall: histogram is univariate; y-axis is always frequency, so we don’t need a y=_ mapping
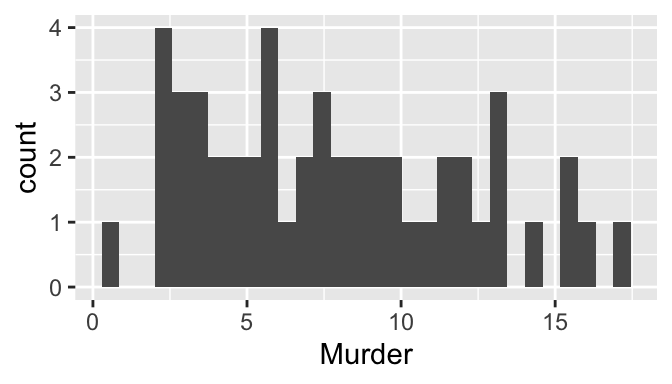
- Can add arguments in geoms
- Note the differences in the syntax convention:
- base R col vs ggplot fill
- base R border vs ggplot color
- esp. “color” (ggplot) vs “col” (base R)
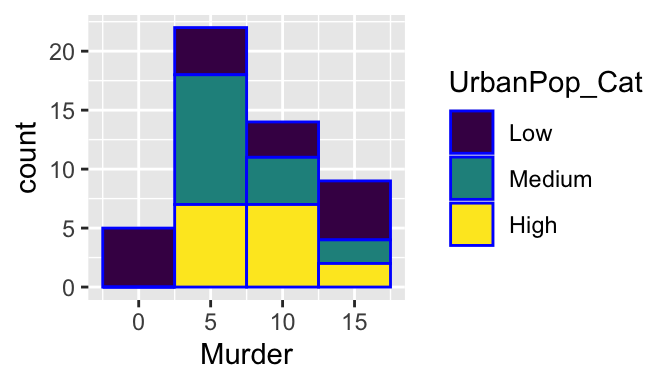
- Add another dimension (i.e., map another variable to another aesthetic)
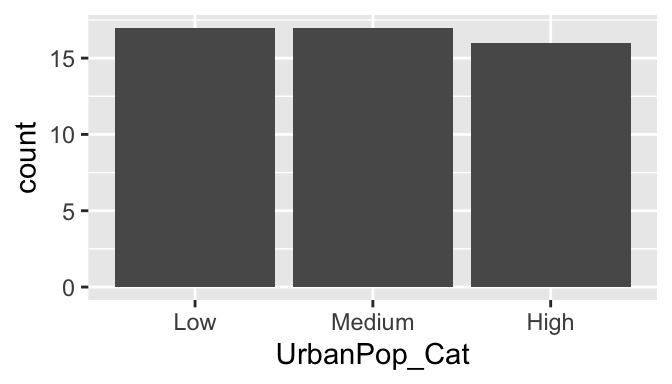
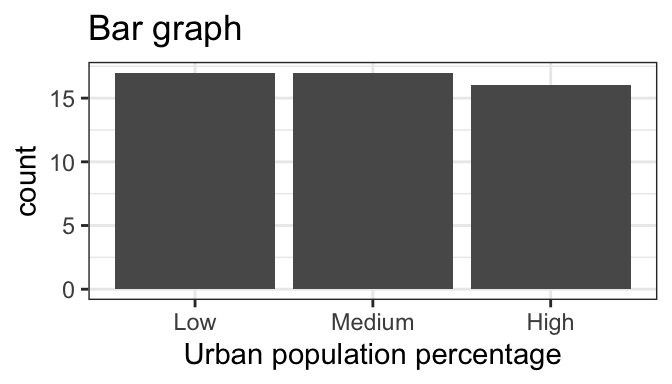
geom_bar
- The bar graph shows that each category has roughly the same number of states, as expected.
geom_text
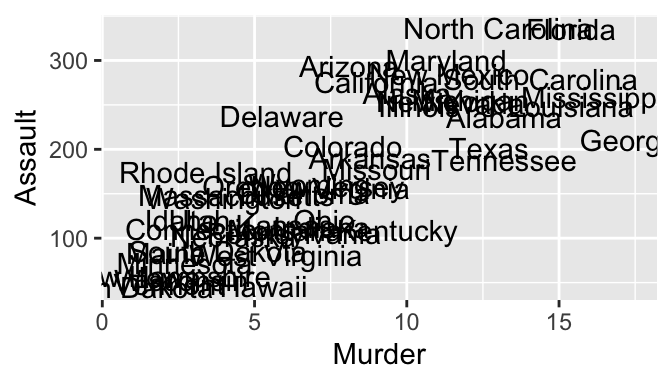
- Try: change geom_text to geom_label
- Try: add geom_point
Customize ggplot with +
ggplot offers a very convenient syntax (+) to add elements and layers
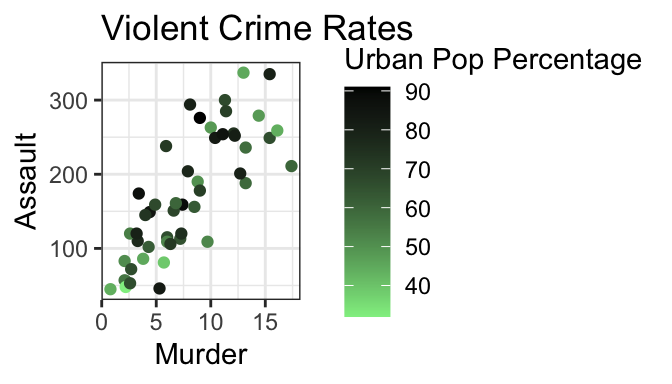
Example: change gradient color
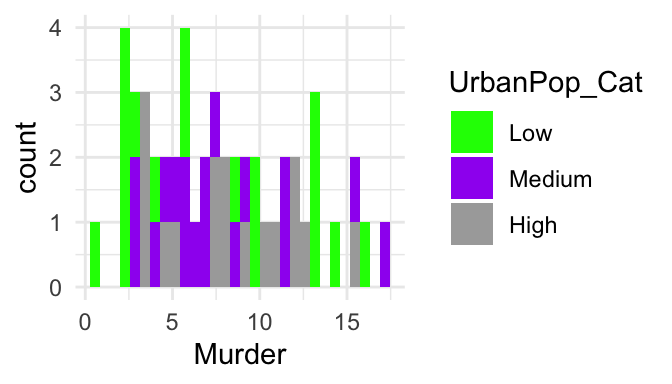
Example: change categorical color
There’s more!
- There are many other geoms and customization available!
- Each geom has its own set of aesthetics to which variables can be mapped.
- Bring up the help page to check what aesthetics are needed.
- Many references can be found online - they all share the same, unified structure that you can now understand.
Data manipulation: tidyverse
The Pipe operator
tidyverse packages: https://www.tidyverse.org/packages/
Powerful and popular for working with complicated dataset, typically formatted into a tidy format
Importantly, the pipe operator offers a new way of calling a function
These three lines of code are equivalent
- Functions in tidyverse are typically used with the pipe operator, but this is not required. For instance, these code are equivalent
Useful tidyverse functions
# filter: subset data according to some condition
USArrests |>
filter(UrbanPop_Cat=='High', Murder > 10)
# slice: subset specific rows
# select: subset specific columns
USArrests |>
slice(1:5) |>
select(Murder,Assault)
# arrange: sort by a variable
USArrests |>
arrange(desc(Murder)) |>
slice(1:5)
# summarise: calculate summary statistics
USArrests |>
summarise(mean(Murder),median(Murder),count=length(Murder))
# mutate: create new variables
USArrests |>
mutate(Violent = Murder + Assault + Rape) |>
arrange(desc(Violent)) |>
select(Violent)
# group_by: look at subset groups of data
USArrests |>
group_by(UrbanPop_Cat) |>
summarise(mean(Murder), median(Murder))Integration with ggplot
- The pipe operator works very well with ggplot syntax
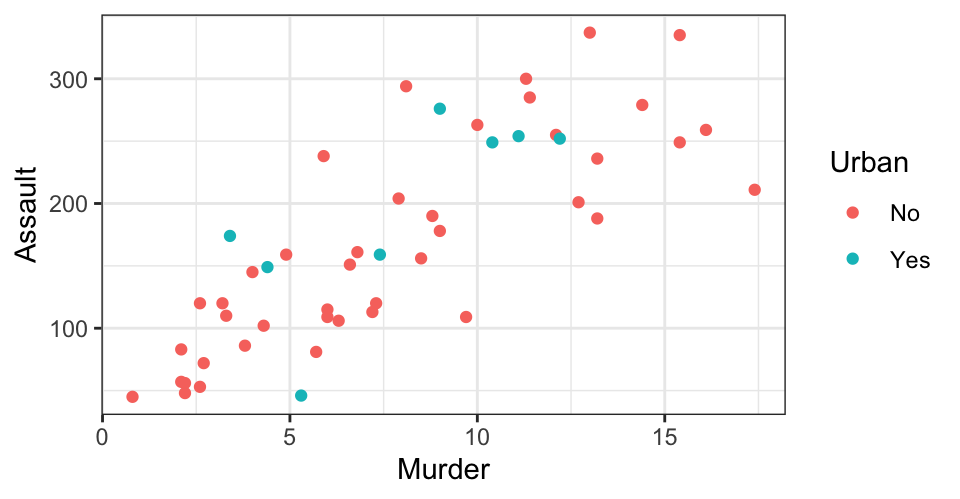
Combine data: map example
Map
- There are a few different maps included in the maps package
- What exactly is mymap? Try some basic visualizations…
Combine data
- We want to combine the following dataset
- The “State” column in USArrests should match the “region” column in mymap; the state names should have consistent spelling and capitalization
Murder Assault UrbanPop Rape State UrbanPop_tile UrbanPop_Cat
Alabama 13.2 236 58 21.2 Alabama 1 Low
Alaska 10.0 263 48 44.5 Alaska 1 Low
Arizona 8.1 294 80 31.0 Arizona 3 High long lat group order region subregion
1 -87.46201 30.38968 1 1 alabama <NA>
2 -87.48493 30.37249 1 2 alabama <NA>
3 -87.52503 30.37249 1 3 alabama <NA> long lat group order region subregion Murder Assault UrbanPop Rape
1 -87.46201 30.38968 1 1 alabama <NA> 13.2 236 58 21.2
2 -87.48493 30.37249 1 2 alabama <NA> 13.2 236 58 21.2
3 -87.52503 30.37249 1 3 alabama <NA> 13.2 236 58 21.2
UrbanPop_tile UrbanPop_Cat
1 1 Low
2 1 Low
3 1 LowVisualization!
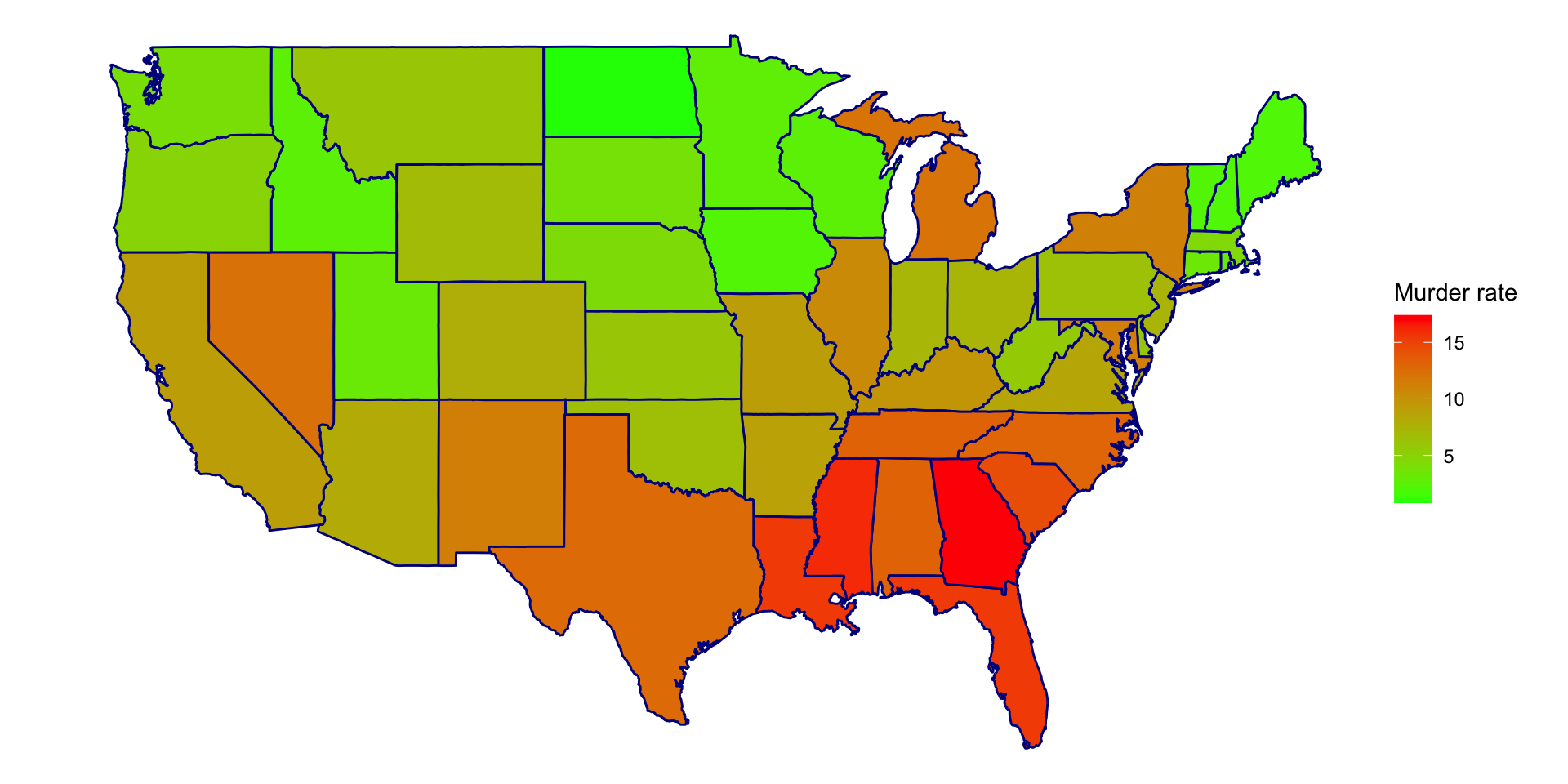
Different ways to join data
- Run ?left_join() to understand different ways to join data.
- Discussion: what will the following code return? You can run the code to find out.
name exam project
1 A 80 1
2 B 91 2
3 C 85 1
4 D 78 NA projectID description
1 1 visualization
2 2 classification
3 3 text mininginner_join(df.student, df.project, by=c('project' = 'projectID'))
left_join(df.student, df.project, by=c('project' = 'projectID'))
left_join(df.project, df.student, by=c('projectID' = 'project'))
right_join(df.student, df.project, by=c('project' = 'projectID'))
full_join(df.student, df.project, by=c('project' = 'projectID'))